Hard water or soft water? What type of water should athletes be drinking, and when?
Water is one of the most versatile tools athletes can use in their daily quest to augment performance and achieve longer, more fulfilling careers. As such, there is more than one way to drink it. Let’s talk about some of the ways that you can drink water to make it do more for your body.
Hard water vs. Soft water: Large and in “Charge”
Micronutrients in the form of minerals are vital to athletes. Without them, vitamins cannot do their job and the macronutrients that we eat will be less able to help us recover from muscle damage or to refuel muscle tissue. Athletes in particular are susceptible to greater mineral deficiencies than most people. They bleed through their mineral reserves more quickly because of the stress inherent to exercise and exertion, and it is difficult if not impossible to keep up with their need to replenish these minerals from food alone. As an example, the literature is clear that there can be a one-hundred fold difference between someone ingesting enough of a mineral to avoid being deficient versus ingesting enough of a mineral to optimize the function of that mineral in the body.
That being said, the “hardness” or “softness” of water refers to the water’s mineral content. Minerals receive their electric charge (ie. electrolytes) when dissolved in water, and water can provide a more reliable and bioavailable source of minerals than food. The main reasons for this are that in the 21st century our soils produce foods with a 30% to 40% decreased mineral content compared to the soils seventy or eighty ears ago. Also, foods can contain compounds such as phytonutrients and phytates which interfere with the absorption of minerals. Hard water bypasses both of these issues, and when ingesting minerals via hard water none of the minerals are lost to stool.
Generally speaking, the harder the water, the more minerals it contains (namely sodium, calcium, and magnesium, but also other trace minerals such as zinc, copper, chromium, and sulphur), and the softer the water, the less minerals it contains. Wherever possible, athletes should choose harder water sources. Of course, not all hard water is created equal and they can differ greatly in mineral concentration.
The Water Rules
Here are some of the types of essential minerals to look for in water- and when. Remember that essential minerals are minerals that the body must obtain from external sources, as it cannot produce them on its own
1. Sodium
Since electrolytes like sodium determine how water is used and stored in the body, I always advocate that athletes weigh themselves pre-activity, monitor their weight post-activity, and prepare their own hard water solution containing 3 cups of water and ¼ tsp of pink salt for every pound of bodyweight that has been lost. This is an effective formula for ensuring that athletes are properly rehydrated following training and competition because sodium (salt) is lost alongside water in the sweat.
Aside from re-hydration, sodium-rich hard waters- especially those also containing potassium – can be used with meals (preferably beforehand). This is because sodium and potassium are important components of stomach acid, and drinking soft water around meals can dilute the acid in the stomach- inhibiting the digestive process. This is particularly important for athletes on “vertical” or high-calorie diets. The more food you ingest, the more sodium is required in the diet. Do not drink soft water around or with your meals. Instead, drink water providing a generous amount of sodium to ensure that you absorb as many nutrients as possible from the food you eat, and to avoid leaving bits of undigested food to ferment and cause problems within the stomach and bowels. Sodium also increases insulin sensitivity, ensuring that the foods you replenish the body with post training/competition effectively make their way into fatigued muscle cells.
Lastly, a healthy intake of sodium will also help prevent the loss of the following two minerals, in general.
2. Magnesium
Involved in over three hundred physiological processes, this is the number one mineral that is deficient in athletes and it plays a pivotal role in regulating many things: sleep, muscle/tissue repair, heart rate, mitochondrial health, insulin resistance, and cellular pH. Optimal levels of magnesium for active people may be difficult to get from food sources alone – soil quality notwithstanding. But magnesium-rich hard water can provide north of 400mg/day and contribute significantly to your total dietary magnesium.
A good equation for determining how much magnesium one needs is 7.5mg – 10mg per kg of body weight, a formula recommended by Dr. James Lavalle. The more active an athlete, the closer to the 10mg range they should be. We have had success using this formula to decrease markers of athlete stress, improve sleep and thus, improve training outcomes.
Athletes are also prone to constipation because they tend to have higher cortisol (stress) levels, but magnesium-rich hard water can also be used to help solve this problem. The regular drinking of this hard water is one of the BEST things athletes can do get the most out of their training and recovery schedule so that, come game day, they can capitalize on all of their hard work. Hard water magnesium may be absorbed into the body even more effectively than supplemental magnesium, and it is easier to divide throughout the day simply by sipping- which further increases absorption.
3. Calcium
Calcium is needed to facilitate muscle contractions, but it can also help maintain a healthy body composition by limiting the growth of fat cells (once again, important for athletes on vertical or high-calorie diets), and it can even help reduce Premenstrual Symptoms (PMS). Not all people can enjoy milk products because of the high prevalence of lactose intolerance present in the population, and thus many may not be getting enough calcium. Using calcium-rich hard water to help you reach 1000mg to 1200mg of calcium per day is an effective alternative to dairy.
4. Trace Minerals
Don’t forget that hard water also contains trace minerals in the form of chromium, zinc, copper, potassium, and sulphur. These trace minerals can also be lost through stress and exercise, and play an important role in general health and performance.
The Bottom Line
When it comes down to it, mineral water is even better at rehydrating the body post-activity than many sports drinks, and there is evidence to suggest that it also enhances subsequent muscle performance – especially sulphurous hard water (hard water containing forms of sulphide), which can protect against oxidants and exercise-induced muscle damage. The main takeaway is that drinking harder water as a general practice can improve overall metabolism (the creation of energy in the body) and help people stay prepared for sport and recreational activity.
Where can you purchase hard water?
Here are three lists of brands which produce hard water for purchase (from left to right, the columns are Magnesium, Sodium, and Calcium. All numbers are milligrams per liter):
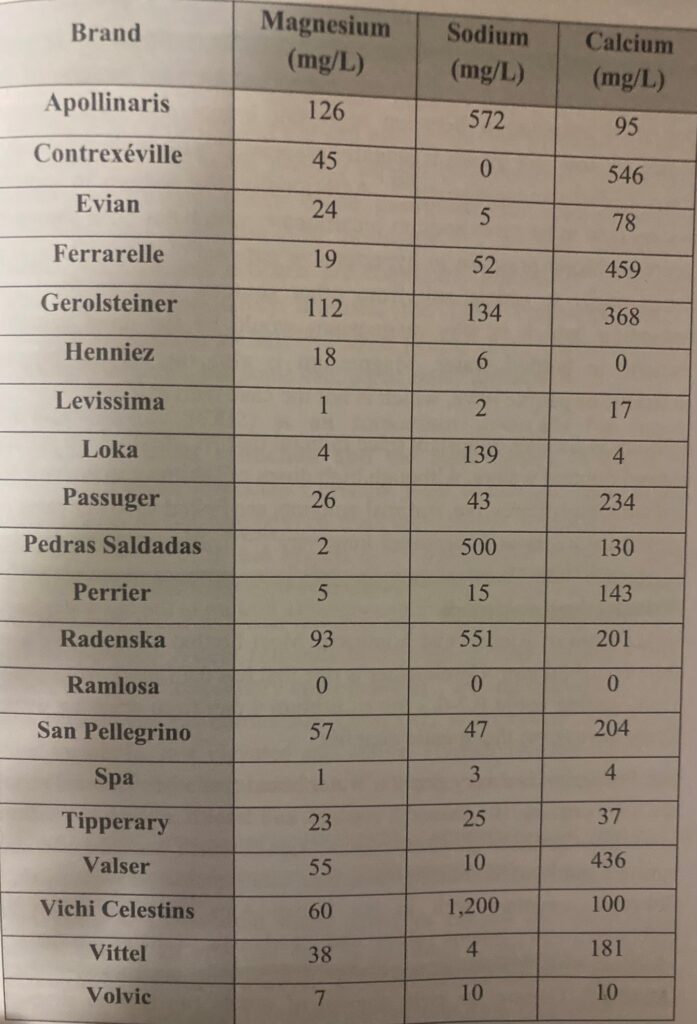
Adapted from Garzon and Eisenberg (1998) ‘Variation in the mineral content of commercially available bottled waters: implications for health and disease’
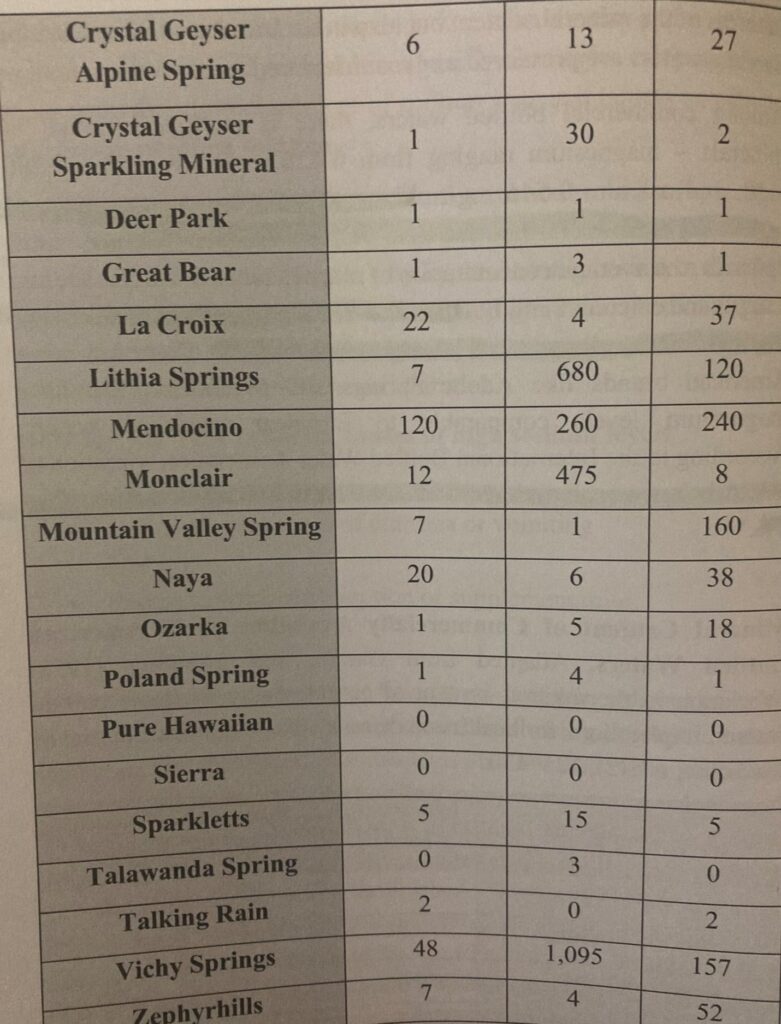
Adapted from Weisenberger (1991) ‘The Pocket Guide to Bottled Water’
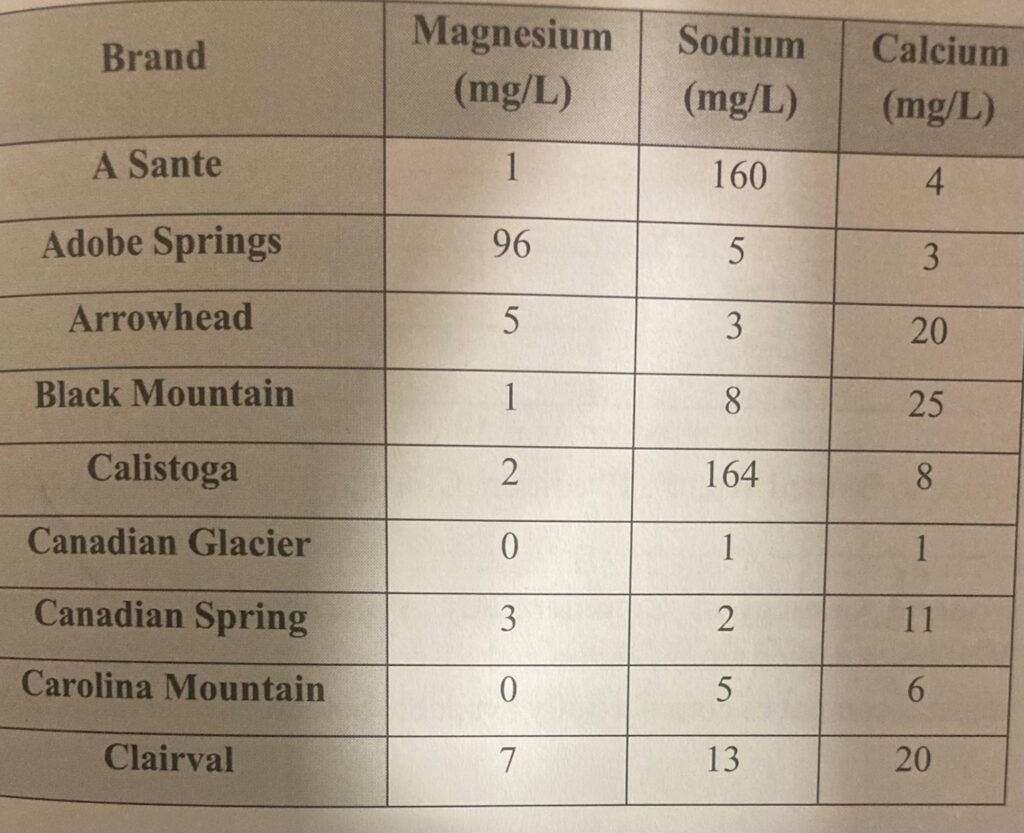
Adapted from Green and Green (1994) ‘The Good Water Guide’
Happy Training.
#sportsnutrition #torontosportsperformance#axisperformanceandtraining #beyperformance #onlinetrainer #onlinetraining#personaltrainer #strengthcoach #torontopersonaltrainer #torontostrengthcoach #hydration